Note:
The dialog for each function has a Help Tab that contains the full help topic for the current function.
The easiest way to get the syntax for an ArcPy script is to create a model in ArcGIS Desktop using the ET Surface tools. Then export the model as a Python script. Unfortunately in ArcGIS Pro you cannot export your model as Python script. Below is a sample model using the ET Surface tools and the corresponding python script.
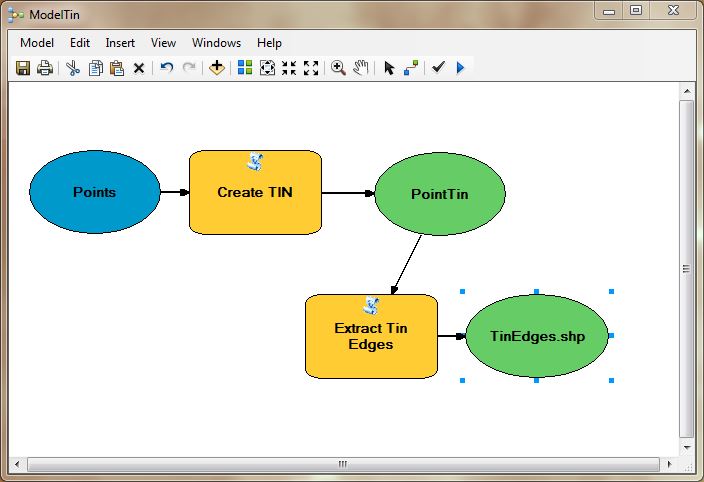
| # Import arcpy module import arcpy # Load ET Surface Toolbox arcpy.ImportToolbox("C:/testToolBox/ETSurface70.pyt") # Local variables: input = "C:\\TestData\\Points.shp" elevationfield = "Elevation" triangulation = "Point" result1 = "C:\\TestData\\PointTin" result2 = "C:\\TestData\\TinEdges.shp" # Process: CreateTin arcpy.CreateTin_ETSurface(input, result1, elevationfield, triangulation) # Process: Extract TIN edges arcpy.ExtractTinEdges_ETSurface(result1, result2, "true") |