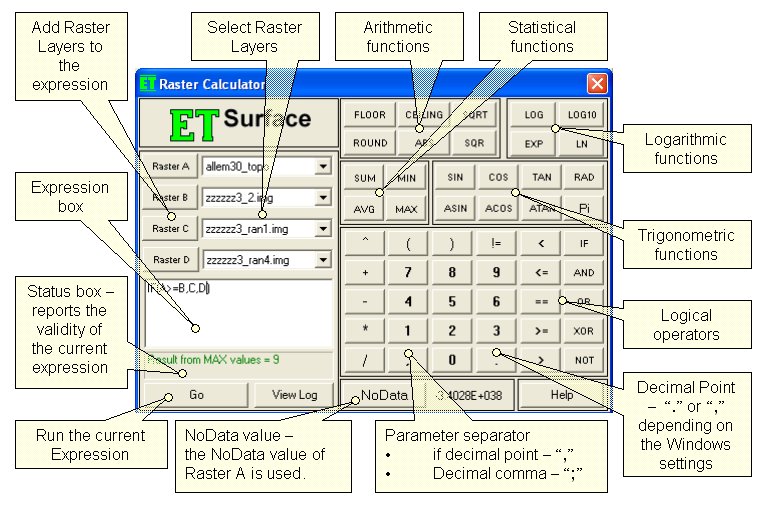
Inputs:
- Rasters - up to 4 rasters can be used. If the Raster Calculator is used from the GUI, the rasters are selected from the raster layers loaded in ArcMap. In the ToolBox implementation the input can be a raster layer or raster dataset. The 4 rasters are called Raster A, Raster B, Raster C and Raster D. Raster A is required, the other rasters are optional.
- Expression - the formula to be used for the calculation to be performed. For shortness the rasters should be entered with their letters in the expression - A for Raster A, B for Raster B, etc. All the functions available can be typed in the expression box or selected from the calculator buttons provided. The functions are not case sensitive - SIN, Sin and sin will be accepted as correct entries. Note that the operator for EQUAL is "==" and NOT "=" (which is operator for assignment). The syntax of all functions is discussed below.
Output:
- If the Raster Calculator is used from the GUI, the raster dataset created when an expression is executed is a temp raster and is stored in the temp folder of ET Surface. If you want to save it as a permanent raster, use the Export Data tool.
- If the ToolBox implementation is used, the user is asked for an output name and location and the raster dataset created is permanent.
- The output raster dataset
will
- Be FLOAT type
- Have the cell size of the Raster A (if any of the other rasters used have a different cell size, it will be resampled)
- The extent will be calculated as the intersection of the extents of the input rasters.
Functions and operators:
- Arithmetic
- FLOOR - Returns the largest integer less than or equal to a number. FLOOR (3.66) = 3
- CEILING - Returns the smallest integer greater than or equal to a number. CEILING (3.15)= 4
- ROUND - Rounds a number to the nearest integer. ROUND (3.66) = 4, ROUND (3.15) = 3
- ABS - Returns the absolute value of a number. ABS(-14) = 14
- SQRT - Returns the square root of a number. SQRT(4) = 2
- SQR - Returns the square of a number. SQR(2) = 4
- Trigonometric
- Pi - adds constant Pi to the expression
- RAD - converts an angle in degrees to an angle in radians.
- SIN - Returns the sine of an angle. The argument should be in radians. SIN(Pi/6) = 0.5; SIN(RAD(30)) = 0.5
- COS - Returns the cosine of an angle. The argument should be in radians. SIN(Pi/3) = 0.5, COS(RAD(60)) = 0.5
- TAN - Returns the tangent of an angle. The argument should be in radians. TAN(RAD(45)) = 1
- ASIN - Returns the angle (in radians) whose sine is the specified number. To convert the result to degrees multiply with 180/pi - ASIN(0.5)*180/Pi = 30
- ASIN - Returns the angle (in radians) whose cosine is the specified number.
- ATAN - Returns the angle (in radians) whose tangent is the specified number.
- Logarithmic
- LOG - Returns the logarithm of a number.
- LOG10 - Returns the base 10 logarithm of a specified number.
- LN - Returns the natural logarithm of a number.
- EXP - Returns e raised to the specified power.
- Statistics
- SUM - Returns the sum of the arguments - SUM(1,2,3,4,5) = 15
- MIN - Returns the minimum of the arguments - MIN(1,2,3,4,5) = 1
- MAX - Returns the maximum of the arguments - MAX(1,2,3,4,5) = 5
- AVG - Returns the average of the arguments - AVG(1,2,3,4,5) = 3
- Logical
- IF - logical if. The syntax is IF(expression, true result, false result) - IF(2>1,100,200) = 100
- != - Not equal - IF(2 != 1,100,200) = 100
- == - equal - IF(2 == 1,100,200) = 200
- AND - logical and - IF(2 > 1 AND 3 == 4,100,200) = 200
- OR - logical or - IF(2 > 1 OR 3 == 4,100,200) = 100
- XOR - logical xor - IF(2 > 1 XOR 3 == 4,100,200) = 100
- NOT - logical not - IF(NOT(2 == 1),100,200) = 100
Priority of the operators
| Priority | Operators |
| 1 | AND, OR, XOR |
| 2 | ==, !=, <=, >=, <, > |
| 3 | +, - |
| 4 | *, / |
| 5 | ^ |
NoData Values
- The NoData value of the output raster will be equal to the NoData value of raster A
- If any of the rasters participating in an expression have NoData value in certain location, the output will have NoData value at this location
- The user can use NoData in an expression to set portions of the output raster to NoData. Example: IF(A<1500,NoData,A) - this expression will create a raster in which all cells with values less than 1500 will be assigned to NoData, the rest of the cells will have the values of the input raster A.
- To replace the NoData values of a raster with valid values use the Replace NoData function.
Command line syntax
ETS_GPRasterCalculator <Raster_A> {Raster_B} {Raster_C} {Raster_D} <out_raster>,<Expression>
Parameters
| Expression | Explanation |
|---|---|
| <Raster_A> | A Raster dataset or Raster layer |
| {Raster_B} | A Raster dataset or Raster layer |
| {Raster_C} | A Raster dataset or Raster layer |
| {Raster_D} | A Raster dataset or Raster layer |
| <out_raster> | A String - the full name of the output raster (Araster with the same full name should not exist) |
| <Expression> | A String - the expression to be executed |
Example: ETS_GPRasterCalculator elev1 # # # c:\test\output.img IF(A > 1300, NoData, A)
Scripting syntax
ETS_GPRasterCalculator (Raster_A, Raster_B, Raster_C, Raster_D, out_raster, expression)
See the explanations above:
<> - required parameter
{} - optional parameter
RasterCalculator (rasterDatasetA As IRasterDataset2, rasterDatasetB As IRasterDataset2, rasterDatasetC As IRasterDataset2, rasterDatasetD As IRasterDataset2, sOutRaster As String, sExpression As String) As IRasterDataset2
The Raster Calculator uses the free MuParser © Ingo Berg (see license).